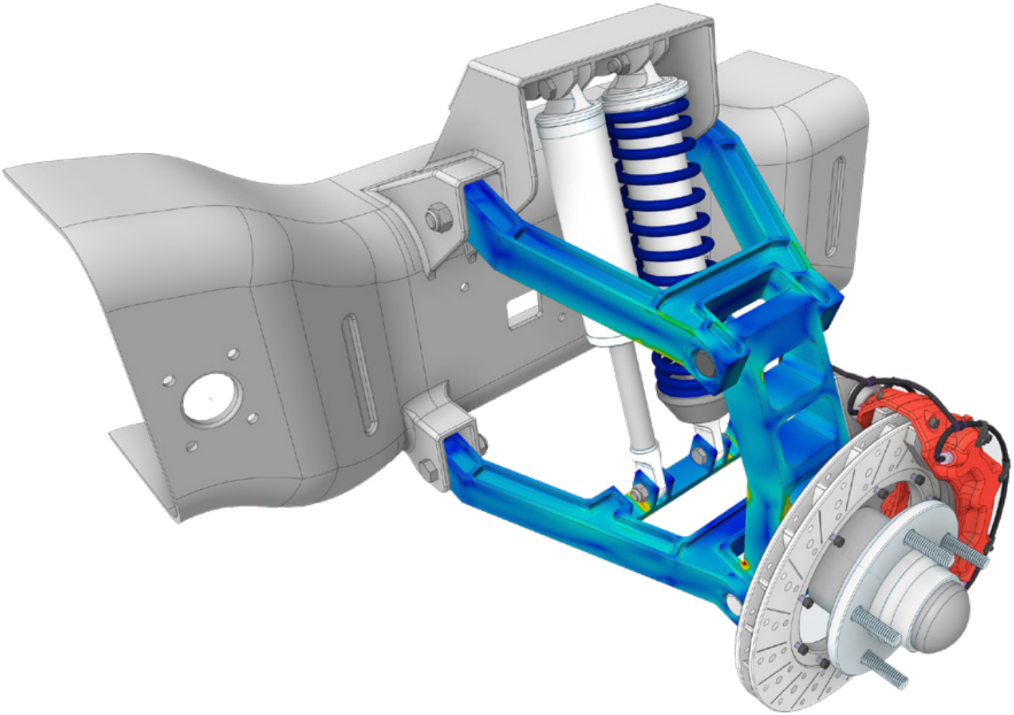
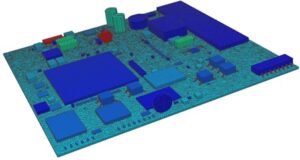
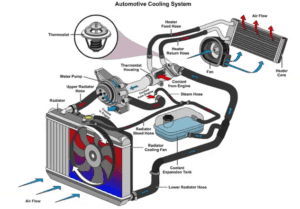
Ansys Mechanical Webinar | Mechanical Reliability Prediction
Learn how to improve product reliability and performance while meeting the challenging demands that customers put on electronic devices. Ansys Mechanical’s comprehensive multiphysics solvers provide solutions for predicting mechanical reliability. That is, everything from individual components to printed circuit boards to complete device and systems. Whether you are testing thermal or mechanical reliability, Ansys Mechanical can help meet your design goals while reducing the need for physical prototypes.
Need Help Predicting Mechanical Reliability for Electronics?
This webinar will explore various mechanical reliability challenges such as thermal cycling, drop and impact simulations, shock and vibration analysis, life prediction, and warranty cost reduction.
Learn how Ansys Mechanical can help you meet your design requirements while significantly reducing the high cost of physical testing!
Logistics Engineering & Reliability
Reliability in logistics engineering and management can be defined as the likelihood that a system or product will function as intended for a predetermined amount of time, when used under predetermined operating conditions.
Reliability engineering places an emphasis on delivering satisfactory performance throughout a product’s lifecycle. Effective reliability engineers must have a baseline degree of expertise across all technical disciplines as well as a grasp of failure mechanisms gained from experience and applied knowledge. After all, engineering in its most useful form is reliability.
In the past, products were overdesigned to increase their reliability. In terms of predicting mechanical reliability, first understanding prevalent failure types and material characteristics was lessened by this process.
Mechanical Reliability in the Modern Age
Mechanical reliability is seen very differently today. Today’s designers do not have the luxury of overengineering because of stringent consumer demands, the importance of weight (especially in airplanes), and the expense of the product.
There are several analysis and prediction methods available nowadays, which makes the reliability engineering environment more complicated. The availability of cutting-edge material data and statistical modeling methods using a variety of software tools and computing benefits is the source of these distinct approaches.
Various approaches additionally make use of a variety of variables that can better model factors like manufacturing quality, material variances, system complexity, and design tolerances. We suggest a method that applies the Systems Engineering mindset and immediately narrows the focus to only those analysis activities that deliver the needed insights in order to manage today’s reliability engineering efforts.
Traditional Reliability Analysis Methods
Engineers frequently use program requirements as a reference for creating fielded reliability estimates or projections. The reliability analysis process, shown in Figure 1, takes into account reliability over a distribution of failures and typically entails the following steps:
- Recognize the design specifications
- Describing the system’s hardware configuration and its characteristics
- Define the operational conditions for the system.
- Define the mission profile and system usage rate.
- Create a mechanism for dependability prediction
- Actively putting reliability prediction to use
- Write up the findings and highlight the conclusions.
Predicting Mechanical Reliability | Methodology
The reliability study of mechanical components has specific difficulties in establishing reliability prediction systems. Analytical models that characterize the fundamental dependability of each component type and take operating conditions into account exist for electronic devices. The electronic prediction methodology is implemented by other software applications as well, such as Ansys Redhawk.
Regrettably, there is no “universal” methodology that can be used to forecast the reliability of mechanical components. Most mechanical parts and assemblies experience wear throughout the course of their lives, unlike electronic parts. The exponential (constant failure rate) reliability approach used in electronic prediction methodology is one of the major reliability prediction models that suffers from this limitation.
Additional Ansys Software Tips & Tricks Resources
-
- Analyzing normal and Tangential Elastic Foundations in Mechanical
- Why Meshing is Crucial for FEA Fluid Simulations Prior to Prototyping
- For support on Contained Fluid FEA Modeling with HSFLD242 Elements
- For Exporting a Deformed Geometry Shape Post-Analysis in Mechanical
- Moreover, for guidance Multi-Step Analyses in Mechanical
- For Retrieving Beam Reaction Force in a Random Vibration Analysis
- Deploying Ansys Macro Programming vis *USE Command in Mechanical
- For replicating Fatigue Models from Start to Finish in Mechanical
- In addition, setting up Acoustic Simulations of a Silencer
- For a step-by-step guide on 2D to 3D Submodeling in Mechanical
- For modeling Pipe16 Circumferential Stress in Mechanical
- For Support on performing ‘EKILL‘ in Workbench
- APDL Command Objects post-Spectral Analysis
- For Separating DB Database Files from RST Files
- Measuring Geometric Rotation in Mechanical WB
- Explicitly, CAD Geometry Deformation Plasticity
- Offsetting a Temperature Result to Degrees Absolute
- For general guidance on Ansys Post-Processing
- Finally, for basic Ansys Software Installation and License Manager Updates